Developer Guide
[!] Before reading
To help simplify the understanding of the design of our application – McKitchen – we would be referring to our application as RecipeBook as it makes more intuitive sense
as our application functions similar to RecipeBook which contains a set of Recipe and so on.
With that in mind, let’s begin.
Table of Content
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Implementation
- Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Acknowledgements
- McDonald’s for inspiring our project and logo.
- AddressBook Level-3 from https://se-education.org/ which served as a base for our application.
- JavaFX for the GUI functionality.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Architecture
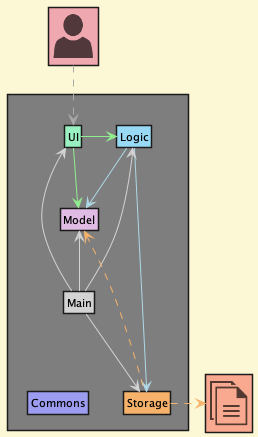
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main has two classes called Main and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to the hard disk.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete Aglio Olio.
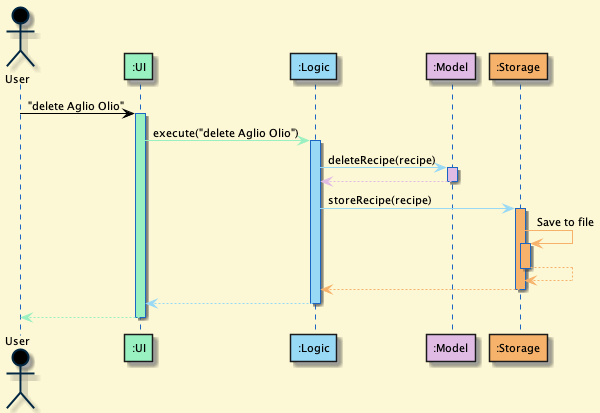
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
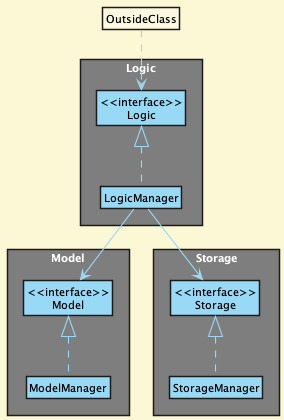
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component’s being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
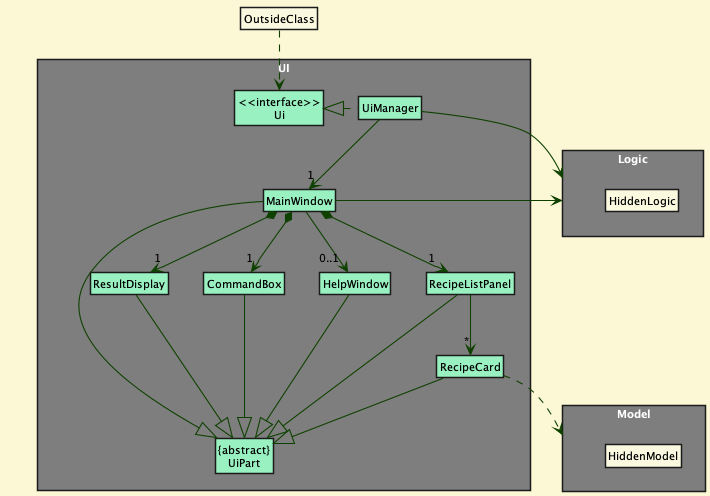
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, HelpWindow,RecipeListPanel etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysRecipeobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here’s a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
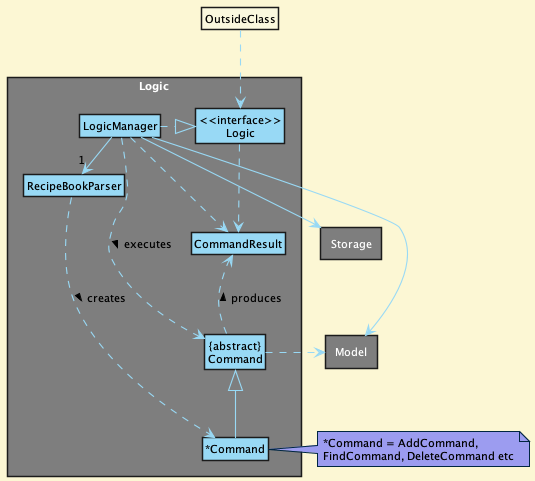
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it uses theRecipeBookParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,AddCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to add a recipe). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned fromLogic.
The Sequence Diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for the execute("delete -x 1") API call.
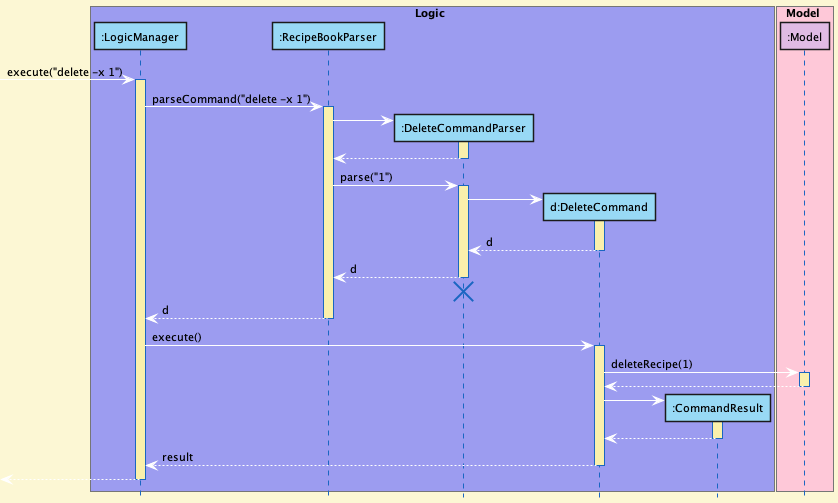
DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
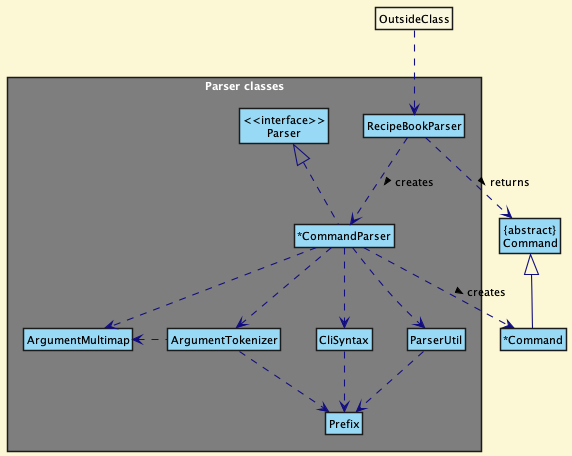
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
RecipeBookParserclass creates an*CommandParser(*is a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create a*Commandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theRecipeBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
*CommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, …) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
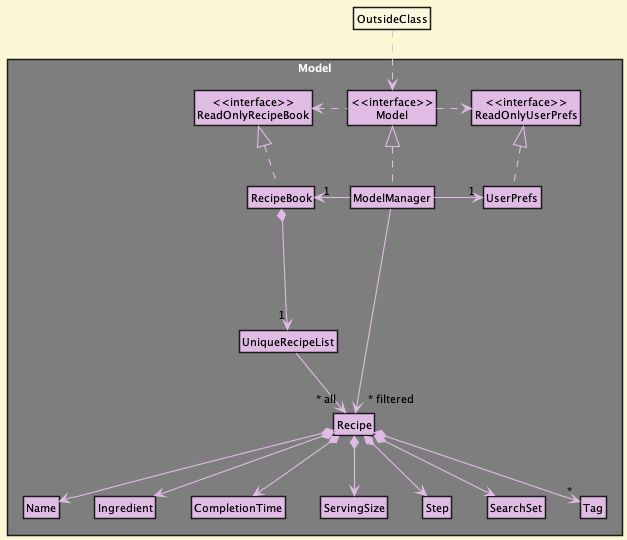
The Model component,
- stores the recipe book data i.e., all
Recipeobjects (which are contained in aUniqueRecipeListobject). - stores the currently ‘selected’
Recipeobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Recipe>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Tag list in the RecipeBook, which Recipe references. This allows RecipeBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Recipe needing their own Tag objects.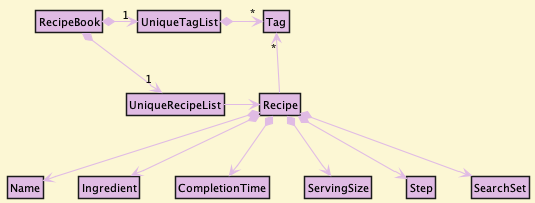
Storage component
API : Storage.java
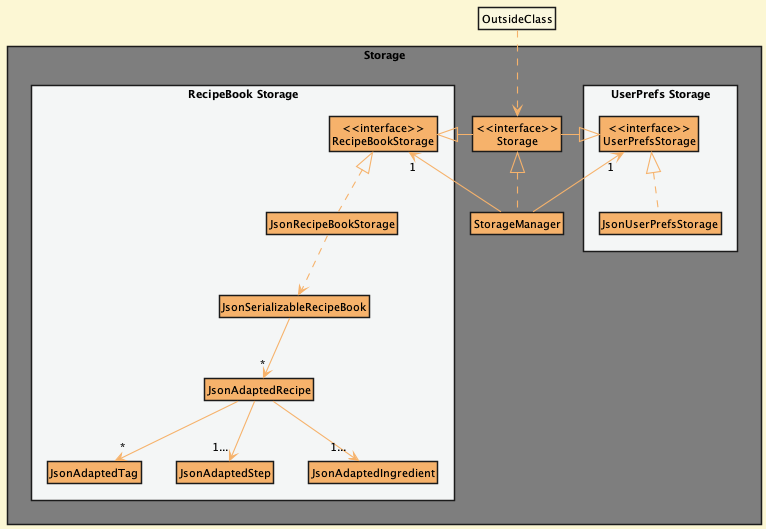
The Storage component,
- can save recipe book data in json format, and read them back into corresponding objects
- can save user preference data in json format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
RecipeBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent’s job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel) - The
JsonAdaptedRecipecontains the standard attributes of aRecipeinJsonPropertyformat. -
JsonAdaptedRecipealso contains attributes in a list such as -
List<JsonAdaptedSteps>,List<JsonAdaptedIngredient>andList<JsonAdaptedTag>format.
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Clear feature
This feature allows the application to clear all the existing recipes in the application. Users will be able to delete all the existing recipes in one command.
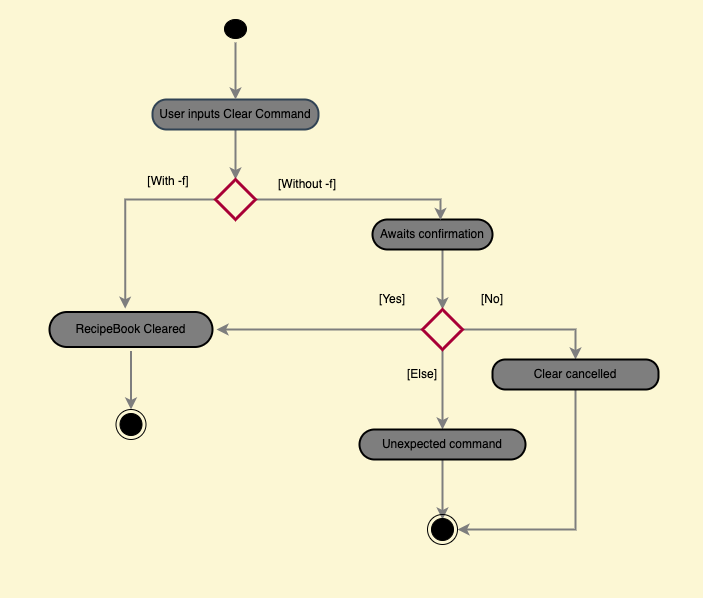
Step 1. The user launches the application.
Step 2. The user executes clear command to clear all recipes.
Step 3. The user will be prompted a yes and no to confirm his clearance
- if the user inputs
yes, the RecipeBook will be cleared - if the user inputs
no, theclearcommand is cancelled. - if the user inputs neither
yesorno, Expected: Unknown Command!Type in the clear command again if you wish to clear
[Proposed] Undo/redo feature
The proposed undo/redo mechanism is facilitated by VersionedRecipeBook. It extends RecipeBook with an undo/redo history, stored internally as an recipeBookStateList and currentStatePointer. Additionally, it implements the following operations:
-
VersionedRecipeBook#commit()— Saves the current recipe book state in its history. -
VersionedRecipeBook#undo()— Restores the previous recipe book state from its history. -
VersionedRecipeBook#redo()— Restores a previously undone recipe book state from its history.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface as Model#commitRecipeBook(), Model#undoRecipeBook() and Model#redoRecipeBook() respectively.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the undo/redo mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The VersionedRecipeBook will be initialized with the initial recipe book state, and the currentStatePointer pointing to that single recipe book state.
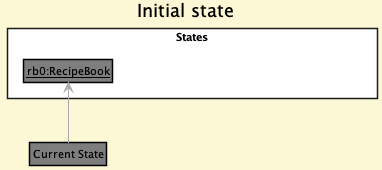
Step 2. The user executes delete -x 5 command to delete the 5th recipe in the recipe book. The delete command calls Model#commitRecipeBook(), causing the modified state of the recipe book after the delete -x 5 command executes to be saved in the recipeBookStateList, and the currentStatePointer is shifted to the newly inserted recipe book state.
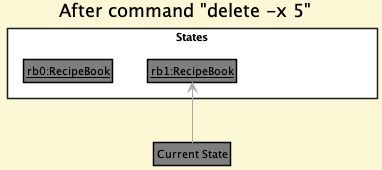
Step 3. The user executes add -n Miso Soup … to add a new recipe. The add command also calls Model#commitRecipeBook(), causing another modified recipe book state to be saved into the recipeBookStateList.
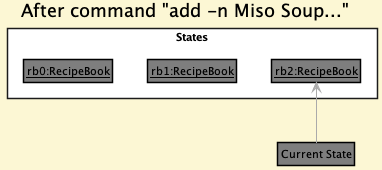
Model#commitRecipeBook(), so the recipe book state will not be saved into the recipeBookStateList.
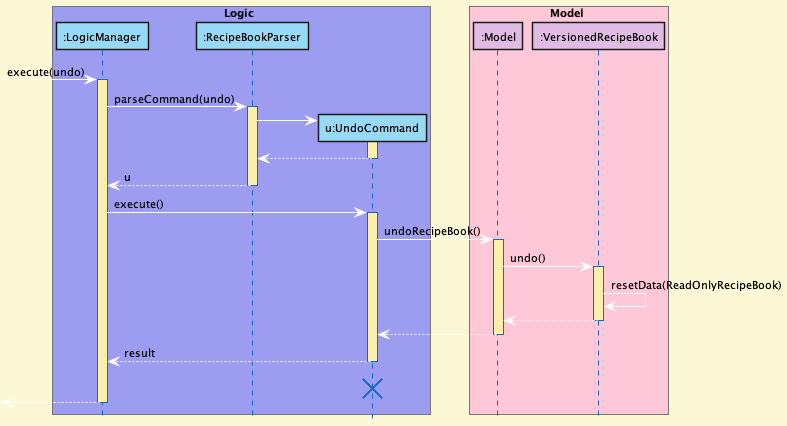
Step 4. The user now decides that adding the recipe was a mistake, and decides to undo that action by executing the undo command. The undo command will call Model#undoRecipeBook(), which will shift the currentStatePointer once to the left, pointing it to the previous recipe book state, and restores the recipe book to that state.
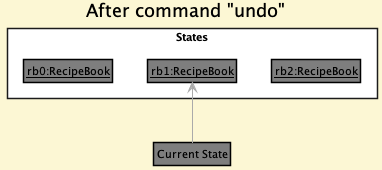
currentStatePointer is at index 0, pointing to the initial RecipeBook state, then there are no previous RecipeBook states to restore. The undo command uses Model#canUndoRecipeBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform undo. The following sequence diagram shows how the undo operation works:
The redo command does the opposite — it calls Model#redoRecipeBook(), which shifts the currentStatePointer once to the right, pointing to the previously undone state, and restores the recipe book to that state.
currentStatePointer is at index recipeBookStateList.size() - 1, pointing to the latest recipe book state, then there are no undone RecipeBook states to restore. The redo command uses Model#canRedoRecipeBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform the redo.
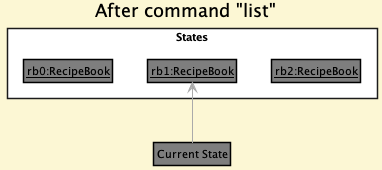
Step 5. The user then decides to execute the command list. Commands that do not modify the recipe book, such as list, will usually not call Model#commitRecipeBook(), Model#undoRecipeBook() or Model#redoRecipeBook(). Thus, the recipeBookStateList remains unchanged.
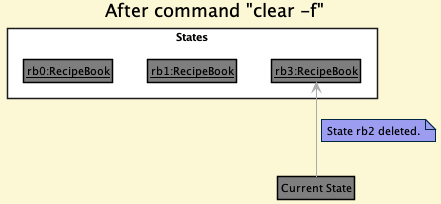
Step 6. The user executes clear -f, which calls Model#commitRecipeBook(). Since the currentStatePointer is not pointing at the end of the recipeBookStateList, all recipe book states after the currentStatePointer will be purged. Reason: It no longer makes sense to redo the add -n Miso Soup … command. This is the behavior that most modern desktop applications follow.
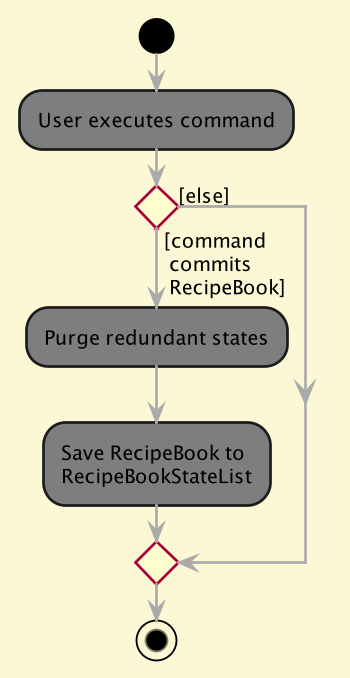
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes a new command
Design considerations
Aspect: How undo & redo executes:
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saves the entire recipe book.
- Pros: Easy to implement.
- Cons: May have performance issues in terms of memory usage.
-
Alternative 2: Individual command knows how to undo/redo by
itself.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
delete, just save the recipe being deleted). - Cons: We must ensure that the implementation of each individual command are correct.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
[Proposed] Advance find feature
The proposed advanced find feature refines how the current find command works by introducing RecipeDoesNotContainKeywordPredicate.
Currently, the purpose of the find feature of our application is to give users the possibility of what Recipe they can cook based on the specified keywords such as recipe name, ingredients available, or cuisine in the form of tags. As such, we would like to improve how the find feature works but allowing the users to specify “must not contain” as part of their keywords to allow greater user experience.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the advanced find would behave.
Step 1. The user launches the application after filling in some recipes and wants to narrow down their search due to their dietary restriction. The user executes find noodle -peanut. The find command separates the user input to 2 sets based on whether it has been prefixed with -.
Step 2. The find command filters out the recipes that match RecipeDoesNotContainKeywordPredicate. In this case, that would mean that it filters out recipes that contain “peanut”.
Step 3. The find command then collects all the recipes that match RecipeContainsKeywordPredicate and displays it to the RecipeListPanel
Miscellaneous guides
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- prefers storing recipes locally to their computer
- wants to be able to quickly access their recipes that they have stored
- wants to experiment with their recipes and adjust them accordingly
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: manage recipes faster than a typical GUI-driven app
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * |
user | be able to see a list of recipes | view all the recipes that I have stored |
* * * |
user | be able to save and load | Automatically see my recently stored recipes |
* * * |
user | be able to view my recipes | see the full details of the recipe such as the ingredients and steps |
* * * |
user | be able to create recipes | add them to the app and save them for later viewing |
* * * |
user | be able to delete recipes from my list of recipes | remove them from a text file in my local computer |
* * * |
user | be able to edit my recipes | make further changes at any point of time |
* * |
user with dietary restrictions | be able to prepare suitable recipes | cook more of them easily |
* * |
student who has online classes at home | cook with what I have at home | save money |
* * |
person who cooks well | be able to export my recipes | share them with people who are curious about a certain dish |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the RecipeBook and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: Add a recipe
Actor: User
Guarantees
- Recipe will be added to a new or existing list of recipes only if the name, completionTime, servingSize, ingredients, steps and tags are valid
MSS
- User requests to add recipes
-
RecipeBook Adds the recipe to a new or existing list of recipes
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. The list is empty.
- RecipeBook creates a new list.
- 2b. The list is not empty.
- RecipeBook checks if the input fields are valid
- If input fields are valid
-
RecipeBook adds recipe
Use case ends.
-
- If input fields are invalid,
-
RecipeBook shows an error message
Use case resumes at step 1
-
- If input fields are valid
- RecipeBook checks if the input fields are valid
Use case: Delete a recipe
Actor: User
Preconditions: User should have an existing list of recipes stored in the local file
Guarantees
- Recipe will be deleted from a list of recipes only if the recipe exists in the recipe list
MSS
- User requests to list recipes
- RecipeBook shows a list of recipes
- User requests to delete a specific recipe in the list
-
RecipeBook deletes the recipe
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. RecipeBook checks if the given recipe index or name is valid.
-
If recipe index or name is valid
Use case ends.
-
If recipe index or name is invalid,
-
RecipeBook shows an error message
Use case resumes at step 2
-
-
Use case: View a recipe
Actor: User
Preconditions: User should have an existing list of recipes stored in the local file
Guarantees
- Recipe can be viewed only if the recipe exists in the recipe list
MSS
- User requests to list recipes
- RecipeBook shows a list of recipes
- User requests to view a specific recipe in the list
-
RecipeBook displays the specific recipe requested by the user for viewing
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. RecipeBook checks if the given index is valid.
-
If index is valid
Use case ends.
-
If index is invalid,
-
RecipeBook shows an error message
Use case resumes at step 2
-
-
Use case: Edit a recipe
Actor: User
Preconditions: User should have an existing list of recipes stored in the local file
Guarantees
- Recipe will be edited only if the recipe exists in the recipe list and fields to be edited are valid
MSS
- User requests to list recipes
- RecipeBook shows a list of recipes
- User requests to edit a specific recipe in the list
-
RecipeBook updates the changes in the recipe
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. RecipeBook checks if the given recipe name or index is valid.
- If recipe name or index is valid
- Use case resumes at step 3b
- If recipe name or index is invalid,
-
RecipeBook shows an error message
Use case resumes at step 2
-
- If recipe name or index is valid
- 3b. RecipeBook checks if the fields to be edited are valid
- if input fields are valid
-
RecipeBook updates specified recipe with input values
Use case ends
-
- if input fields are invalid
-
RecipeBook shows an error message
Use case resumes at step 2
-
- if input fields are valid
Use case: Clear the recipe book
Actor: User
Preconditions: None
Guarantees
- All recipe entries will be cleared from the recipe book.
MSS
- RecipeBook shows a list of recipes
- User requests to clear the list of recipes
- RecipeBook asks for confirmation
- User confirms to clear
- RecipeBook clears all the entries in the recipe book Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. User requests to do a force clear on the list of recipes.
- 2a1. If the entered input contains the forced clear prefix. Use case resumes from step 5.
- 4a. User cancels the clear request.
- 4a1. RecipeBook abort the clear process. Use case ends.
Use case: Find a recipe
Actor: User
Preconditions: None
Guarantees
- Returns a list of recipes that match any of the keywords that the user provided, or
- Informs the user that no recipe matches the keyword that they had provided.
MSS
- User requests to list recipes
- RecipeBook shows a list of recipes
- User requests to search for a recipe based on the keywords provided
- RecipeBook displays a list of recipes that match any of the keywords provided.
Extensions
- 2a. The list is empty
Use case ends - 4a. RecipeBook checks if any of the keywords match any of the recipes inside it
- There are one or more matches
Use case ends. - There are no matches
RecipeBook informs user that there are no recipes that match the keyword(s) provided and shows an empty list of recipes
Use case ends.
- There are one or more matches
Use case: Resets the recipe book
Actor: User
Preconditions: None
Guarantees
- All recipe entries will be cleared from the recipe book and be loaded with the default preloaded recipes.
MSS
- RecipeBook shows a list of recipes
- User requests to reset the list of recipes
- RecipeBook asks for confirmation
- User confirms to reset
- RecipeBook clears all the entries in the recipe book and the recipe book will be loaded with the preloaded recipes. Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. User requests to do a force reset on the list of recipes.
- 2a1. If the entered input contains the forced reset prefix. Use case resumes from step 5.
- 4a. User cancels the reset request.
- 4a1. RecipeBook abort the reset process. Use case ends. —
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 1000 recipes without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Should not use a DBMS to store data.
- Should work without requiring an installer.
- GUI should be usable with resolutions 1280x720 and higher, for screen scales 150%
- Should package everything into a single JAR file
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- DBMS: Database Management System
- GUI: Graphic User interface
- JAR: Java Archive (Java executable file)
- MSS: Main Success Scenario
- Extensions: are “add-on”s to the MSS that describe exceptional/alternative flow of events. They describe variations of the scenario that can happen if certain things are not as expected by the MSS.
- Guarantees: Specify what the use case promises to give us at the end of its operation
- Preconditions: Specify the specific state you expect the system to be in before the use case starts
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the latest McKitchen.jar file and copy into the folder you want to use as the home folder for your McKitchen.
-
To run the application: Open Terminal/Command Prompt in home folder (step 1) and run the following command:
java -jar McKitchen.jar.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app from the Terminal/Command Prompt in home folder and run the command
java -jar McKithen.jar.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
Adding a recipe
-
Adding a new recipe
-
Prerequisites: Prepare a list of required attributes including recipe name, completion time (in mins), serving size (no. of portions), ingredients, steps and tags (optional).
-
Test case:
add -n Recipename1 -d 5 -ss 2 -i IngredientOne 10 spoons | IngredientTwo 5 | IngredientThree 100 grams -s Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 -t Tag1 | Tag2 | Tag3
Expected: A new recipe with the name “Recipename1” with a 5 min completion time, serving size of 2, 10 spoons of IngredientOne, 5 of IngredientTwo and 100 grams of IngredientThree as well as the steps of “Step1”, “Step2” and “Step3” with tags of “Tag1”, “Tag2”, “Tag3”. -
Test case:
add -n Recipename1 -d 5 -ss 2 -i IngredientOne 10 spoons | IngredientTwo 5 | IngredientThree 100 grams
Expected: No recipe is added due to missing recipe steps. Valid command details are shown in the error message. -
Other incorrect add commands to try:
add -n,add,add -ss,add -d,add -s Step2
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
Editing a recipe
-
Editing a new recipe
-
Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
listcommand. Only 9 recipes in the list. Prepare the attributes to be updated. -
Test case:
edit -x 1 -n Recipename1 -d 5 -ss 2 -i IngredientOne 10 spoons | IngredientTwo 5 | IngredientThree 100 grams -s Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3
Expected: Edits recipe with index 1 with a new name of “Recipename1”, completion time of 5, serving size of 2, 10 spoons of IngredientOne, 5 of IngredientTwo and 100 grams of IngredientThree as well as steps of “Step1”, “Step2” and “Step3”. -
Test case:
edit -n Recipename1 -d 5 -ss 2 -i IngredientOne 10 spoons | IngredientTwo 5 | IngredientThree 100 grams -s Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3
Expected: No recipe is edited due to missing recipe index. Error details shown in the status message. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
edit 1,edit -x 1,edit -x 1 -ss,edit -x 1 -d
Expected: No recipe is edited due to missing recipe attributes. Error details shown in the status message.
-
Deleting a recipe
-
Deleting a recipe while all recipes are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
listcommand. Only 9 recipes in the list. -
Test case:
delete -x 1
Expected: First recipe is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted recipe shown in the status message. -
Test case:
delete Aglio Olio
Expected: First recipe is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted recipe shown in the status message. -
Test case:
delete -x 0
Expected: No recipe is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. -
Test case:
delete nuggets
Expected: Recipe does not exist in the recipe book. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete -x -1,delete -x 10,delete 1,delete -x aglio olio
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
Viewing a recipe
-
Viewing a recipe while all recipes are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
listcommand. Multiple recipes in the list. -
Test case:
view -x 1
Expected: Contents of the first recipe is displayed in the result box. -
Test case:
view -x -1
Expected: No recipe is displayed in the result box. Invalid command format error is displayed in the result box with an example showing the correct usage of the view command. -
Test case:
view -x i(where i is larger than the list size)
Expected: Recipe not found message is displayed in the result box. -
Other incorrect view commands to try:
view,view -t,view -s,view -x 0
Expected: Similar to test case 3.
-
Finding a recipe
- Finding a recipe while all recipes are being shown
- Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
listcommand. Multiple recipes in the list. - Test case:
find garlic
Expected: List of recipes will be filtered out to recipes that have garlic as one of their ingredients. - Test case:
find garlic | western
Expected: List of recipes will be filtered out to recipes that have garlic as one of their ingredients or is a western dish. - Test case:
find aglio olio
Expected: List of recipes will be filtered out to recipes that contain “aglio olio”. In this case it is the name of a dish that exists in the recipe book and it would be the only recipe that is shown in the recipe list. - Test case:
find gja390j4fa3
Expected: Result display would show that there are no recipes that match or contain “gja390j4fa3”. This input extends to any arbitrary string that does not match any of the recipe or its contents (name, ingredient, tag).
- Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
Clearing the recipe book
- Clearing the recipe book populated with existing recipes
- Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
listcommand. Multiple recipes in the list. - Test case:
clear -f
Expected: All the recipes will be cleared from the recipe book. - Test case:
clear
Expected: Confirmation prompt shows up, requesting for confirmation.
- Test case:
yes
Expected: All the recipes will be cleared from the recipe book. - Test case:
no
Expected: There will be no changes made to the existing list of recipes.
- Test case:
- Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
Resetting the recipe book
- Resetting the recipe book populated with recipes that are not in the list of preloaded recipes.
- Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
listcommand. Multiple recipes in the list with recipes that are not in the list of preloaded recipes. - Test case:
reset -f
Expected: The recipe book will reset back to the default preloaded recipes and all the recipes that are not in the default preloaded recipe provided by the application are cleared from the recipe book. - Test case:
reset
Expected: Confirmation prompt shows up, requesting for confirmation.
- Test case:
yes- Expected: The recipe book will reset back to the default preloaded recipes and all the recipes that are not in the default preloaded recipe provided by the application are cleared from the recipe book. - Test case:no- Expected: There will be no changes made to the existing list of recipes.
- Test case:
- Prerequisites: List all recipes using the
- Resetting the recipe book populated with an empty recipe book.
- Prerequisites: Clear all the recipes from the recipe book using the
clearcommand. - Test case:
reset -f
Expected: The recipe book will reset back to the default preloaded recipes. - Test case:
reset
Expected: Confirmation prompt shows up, requesting for confirmation.
- Test case:
yes
Expected: The recipe book will reset back to the default preloaded recipes. - Test case:
no
Expected: There will be no changes made to the existing list of recipes and the recipe book will remain empty.
- Test case:
- Prerequisites: Clear all the recipes from the recipe book using the
- Resetting the recipe book with corrupted data in the data json file.
- Prerequisites: Deleting an attribute from a recipe in the json file. For example, deleting the name field for a recipe. Expected: McKitchen contains 0 recipes when the application launches.
- Test case:
reset -f
Expected: The recipe book will reset back to the default preloaded recipes. - Test case:
reset
Expected: Confirmation prompt shows up, requesting for confirmation.
- Test case:
yes
Expected: The recipe book will reset back to the default preloaded recipes. - Test case:
no
Expected: There will be no changes made to the existing list of recipes and the recipe book will remain empty.
- Test case: